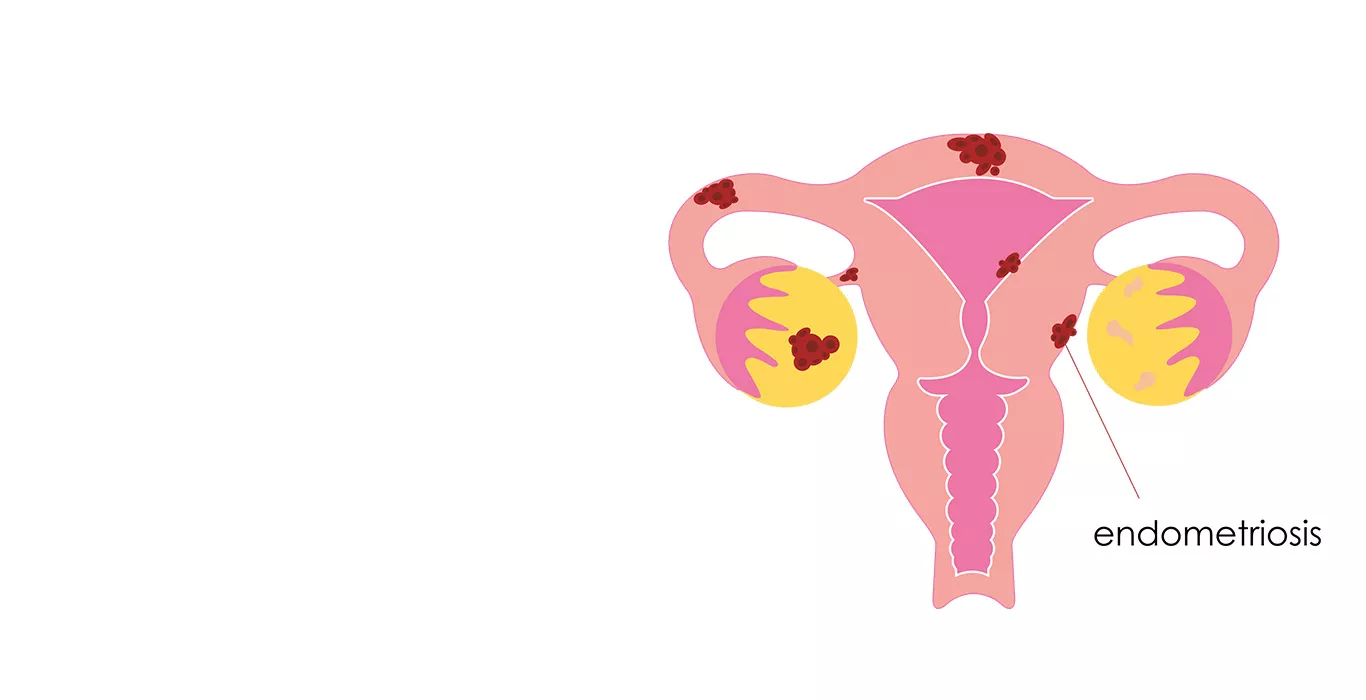
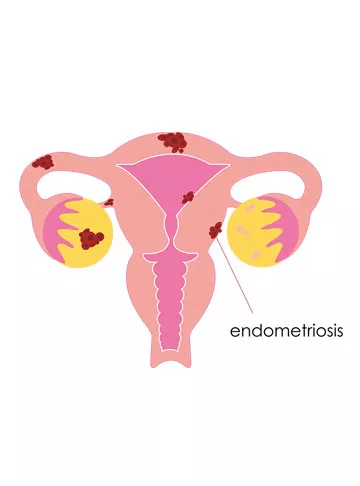
Primary diagnosis of endometriosis may be made upon physical evaluation by a medical practitioner. This has to be further corroborated by more tests.
- Laparoscopy: A laparoscope fitted with a camera is inserted through a little incision into the abdomen to locate endometrial growths, their size, and determine the extent of the problem. To confirm that it is endometrial tissue, a biopsy is performed under a microscope.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the pelvic region helps in the non-invasive visualisation of endometrial growths. In case of endometrioma in ovaries, they may be seen as “chocolate cysts”.
- CT Scan: It is a non-invasive procedure wherein images of the pelvic region are taken. It is an advance imaging technique that combines X-ray and computer technology to produce axial images to pin-point abnormalities, including endometriosis.
- MRI Scan: Another non-invasive imaging technique that produces two-dimensional views of internal structures in the pelvic region, and can help find the organs afflicted by endometriosis.
The treatment of endometriosis is case-based depends on the extent of the disease and needs of the patient. This can be determined after consultation with a healthcare provider after charting health conditions and future aspirations of the patient.
- Medication: Endometriosis can cause immense pain in females afflicted by it. Pain medications such as ibuprofen is prescribed in cases to help subside its effects.
- Hormonal contraceptives & therapy: Since symptoms of endometriosis can be felt due to hormonal changes in the body, hormonal contraceptives may be suggested. This is to reduce the build-up of endometrial tissue induced by hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle in regions where they are present outside the uterus. These can be birth control pills or oral contraceptives, progestin (synthetic form of progesterone), gonadotropin-release hormone agonist that stops production of oestrogen or danazol (synthetic derivative of testosterone).
- Laparotomy: Certain conservative surgery procedures, including laser-based procedures, can be performed to remove “rogue” endometrial growth while keeping the reproductive system intact. This is a preferred treatment option for patients who would like to conceive.
- Hysterectomy: In cases where other treatments do not work and the symptoms do not improve, hysterectomy may be performed to remove organs of the reproductive system, wholly or partly, such as cervix, ovaries and uterus. Conceiving after a hysterectomy, both naturally and using ART, can be eliminated; in such cases, surrogacy may be the way ahead with the female patient’s egg and their husband’s sperm or using donor gametes.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it
Get a free consultation!
© 2025 Indira IVF Hospital Private Limited. All Rights Reserved. T&C Apply | Privacy Policy| *Disclaimer