What are Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)?
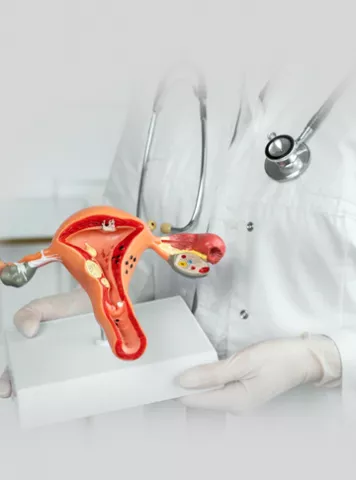
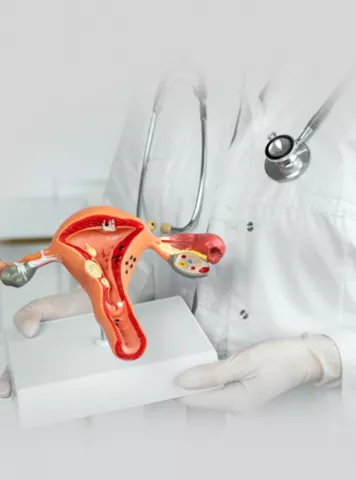
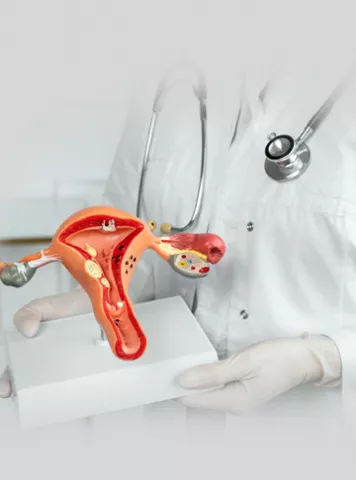
Endometrial polyps, often referred to as uterine polyps, are small, abnormal growths that develop in the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. These growths typically attach to the uterine wall by a thin stalk or a broad base. While they are generally benign or non-cancerous, endometrial polyps can vary in size, ranging from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
Who can get Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)?
Endometrial polyps or uterine polyps can affect women of various ages, but they are more commonly diagnosed in women who are in their perimenopausal or postmenopausal stages. However, they can also occur in younger women of reproductive age.
What are the Types of Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)?
Endometrial polyps can be classified into two main types based on their location within the uterus:
1.Pedunculated Polyps: These polyps are attached to the uterine wall by a thin stalk.
2.Sessile Polyps: These polyps have a broader base and are directly attached to the uterine lining.
What are the Causes of Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)?
There is no concrete cause of endometrial polyps. However, several factors contribute to their development, including:
- Hormonal Factors: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen, during a woman's menstrual cycle, can play a role in the formation of endometrial polyps.
- Chronic Inflammation: Ongoing inflammation in the endometrial lining may trigger the growth of polyps.
- Age and Menopausal Status: As women age, especially during perimenopause and postmenopause, the risk of developing endometrial polyps increases.
-
Obesity: There is a correlation between obesity and the presence of endometrial polyps.
What are the Symptoms of Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps)?
Uterine polyps often present with various symptoms, including:
- Irregular Menstrual Bleeding: This may include heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, irregular menstrual cycles, or bleeding between periods.
- Pelvic Pain: Some women may experience persistent or sporadic pelvic pain not associated with menstruation.
-
Infertility: Endometrial polyps can interfere with fertility by affecting the implantation of a fertilized egg or embryo in the uterus.
-
Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: Some women may notice an abnormal discharge, which can be bloody or watery.
How do Endometrial Polyps affect Female Fertility?
Endometrial polyps or uterine polyps can affect fertility by interfering with the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine lining. They can also disrupt the normal functioning of the endometrium, making it challenging for a pregnancy to establish and progress successfully.
How is Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing endometrial polyps often involves the following procedures:
-
Transvaginal Ultrasound: This imaging technique allows for the visualization of the uterus and the detection of polyps.
-
Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted telescope is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, enabling direct visualization of the uterine cavity and the removal of the polyps for biopsy.
-
Endometrial Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken from the lining of the uterus and examined under a microscope to detect the presence of polyps or any abnormal cells.
How is Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps) Treated?
The treatment of endometrial polyps depends on various factors, including the size and number of polyps, the severity of symptoms, and a woman's reproductive plans. Treatment options include:
- Hysteroscopic Polypectomy: This involves the removal of polyps using a hysteroscope, a minimally invasive procedure.
- Hormonal Medications: Certain hormonal treatments, like hormonal birth control or hormone therapy, may help shrink or prevent the recurrence of polyps.
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): This surgical procedure involves scraping or suctioning the uterine lining to remove the polyps.
Conclusion
Endometrial polyps are common growths in the uterine lining that can lead to various symptoms and, in some cases, affect fertility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options of this condition is essential for effective management. If you suspect you may have endometrial polyps, seeking medical advice and exploring appropriate treatment options is crucial for your overall well-being.
Articles


यूट्रस में गांठ (Bachedani Me Ganth) के कारण, लक्षण और उपचार
कैसे होती है गर्भावस्था के दौ�...

ಗರ್ಭಾಶಯದಲ್ಲಿನ ಫೈಬ್ರಾಯ್ಡ್ನ ಕಾರಣಗಳು, ಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಗಳು ಯಾವುವು?
ಗರ್ಭಾಶಯದ ಫೈಬ್ರಾಯ್ಡ್ಗಳು ಎಂದ�...

గర్భాశయంలో ఫైబ్రాయిడ్ కు కారణాలు, లక్షణాలు మరియు చికిత్స ఏమిటి?
గర్భాశయ ఫైబ్రాయిడ్ లు అంటే ఏ�...

கருப்பையில் உருவாகும் நார்த்திசுக்கட்டிக்கான காரணங்கள், அறிகுறிகள் மற்றும் சிகிச்சை யாவை?
கருப்பை நார்த்திசுக்கட்டி எ�...
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it














