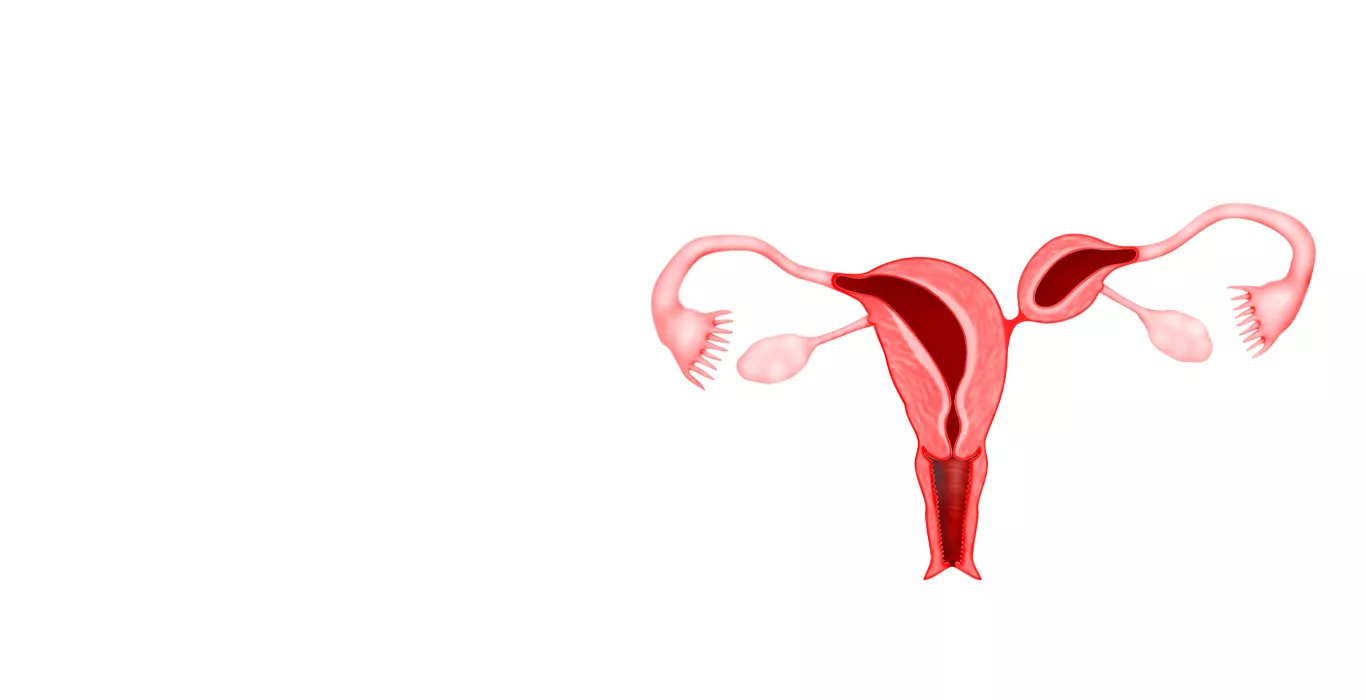
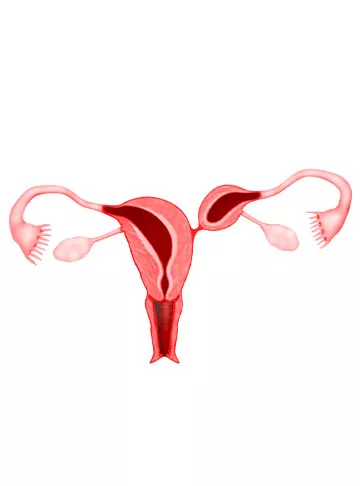
What is Mullerian Duct Anomalies?
Mullerian Duct Anomalies, also known as Mullerian anomalies or congenital uterine abnormalities, refer to structural irregularities in the female reproductive tract. These anomalies arise during embryonic development when the Mullerian ducts fail to develop or fuse correctly, resulting in abnormalities in the uterus, cervix, vagina, or fallopian tubes.
Who can get Mullerian Duct Anomalies?
Mullerian Duct Anomalies are congenital, meaning they are present at birth. They can affect any female, regardless of race or ethnicity. The anomalies can range from mild to severe, and their impact on reproductive health varies from person to person.
What are the Types of Mullerian Duct Anomalies?
There are several types of Mullerian Duct Anomalies, including:
1.Uterine Septum: A band of tissue dividing the uterus partially or completely.
2.Unicornuate Uterus: A uterus that forms only on one side.
3.Bicornuate Uterus: A uterus with two cavities, often with a heart-like shape.
4.Didelphic Uterus: The presence of two uteri and two cervixes, each with its vagina.
5.Agenesis or Absent Uterus: The complete absence of the uterus.
6.Hypoplastic Uterus: A uterus that is smaller than usual.
What are the Causes of Mullerian Duct Anomalies?
The exact causes of Mullerian Duct Anomalies are not always clear, but several factors can contribute to their development:
- Genetic Factors: Anomalies can be inherited or occur due to spontaneous gene mutations.
- Exposure to Drugs or Hormones: Certain drugs or hormonal imbalances during fetal development can disrupt Mullerian duct development.
- Environmental Factors: External factors during pregnancy, such as exposure to toxins or infections, can also play a role.
What are the Symptoms of Mullerian Duct Anomalies?
The symptoms of Mullerian Duct Anomalies can vary based on the specific type and severity of the anomaly. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Changes in menstrual flow or irregular periods.
- Recurrent Miscarriages: Increased risk of miscarriages or pregnancy complications.
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic or cyclic pelvic pain, especially during menstruation.
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Difficulty conceiving or recurrent infertility issues.
Does Mullerian Duct Anomalies Affect Fertility?
Mullerian Duct Anomalies can impact fertility. The severity and type of anomaly determine the extent to which fertility may be affected. Some anomalies can make it difficult to conceive, increase the risk of miscarriages, or cause complications during pregnancy.
How are Mullerian Duct Anomalies Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Mullerian Duct Anomalies typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, imaging studies, and sometimes surgical procedures. Diagnostic methods may include:
- Ultrasound: A pelvic ultrasound can provide valuable information about the structure of the uterus and other reproductive organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is a highly effective imaging technique to visualize the internal structures of the reproductive system in detail.
-
Hysterosalpingography (HSG): This involves injecting contrast material into the uterus and fallopian tubes to detect anomalies and blockages.
-
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure to directly visualize and evaluate the reproductive organs.
How is Mullerian Duct Anomalies Treated?
The treatment for Mullerian Duct Anomalies depends on the type and severity of the anomaly, as well as the individual's reproductive goals. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical interventions, such as hysteroscopic resection, can correct certain anomalies like uterine septum or remove adhesions.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Assisted reproductive technologies like IVF can help individuals with certain anomalies conceive by bypassing or mitigating the structural issues.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormonal treatments may be used to regulate menstrual cycles or improve fertility in some cases.
Conclusion
Mullerian Duct Anomalies are congenital structural irregularities in the female reproductive system that can have a significant impact on fertility and overall reproductive health. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for these anomalies is crucial for individuals facing challenges with their reproductive health. Seeking timely medical attention and exploring appropriate treatment options can greatly enhance the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy and a healthy reproductive life.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it