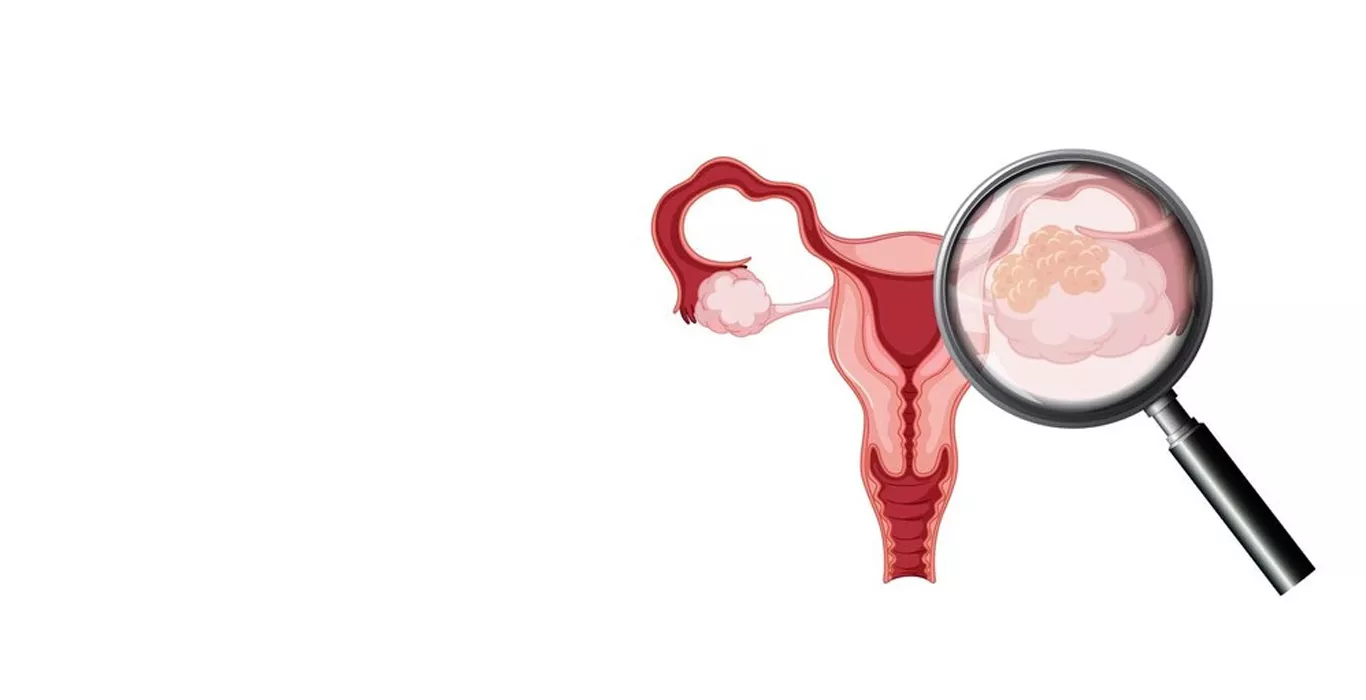
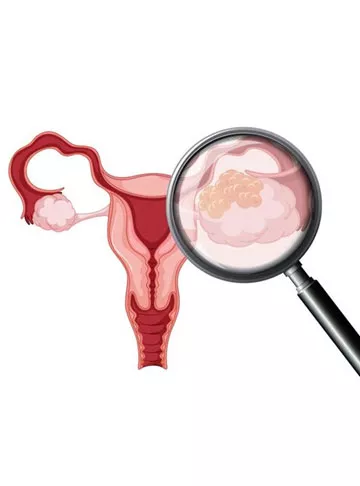
What is Fallopian Tube Cancer?
Fallopian tube cancer, also known as tubal cancer, is a malignancy that starts in the fallopian tubes of a woman's reproductive system. The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the reproductive process, facilitating the transportation of eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. When cancer develops in these tubes, it can spread to other parts of the body, making early detection and treatment critical for a positive prognosis.
Who can get Fallopian Tube Cancer?
Fallopian tube cancer is a rare condition, accounting for less than 1% of all gynaecological cancers. It primarily affects postmenopausal women, with the average age of diagnosis being around 60 years old. However, it can occur in women of any age, including those who have had tubal ligation (a surgical procedure for permanent contraception).
What are the Types of Fallopian Tube Cancer?
The main types of fallopian tube cancer include:
1. Epithelial Carcinoma: This is the most common type, originating from the cells lining the fallopian tubes.
2. Transitional Cell Carcinoma: Less common, this type begins in the cells that make up the lining of the fallopian tubes.
3. Adenocarcinoma: A subtype of epithelial carcinoma, adenocarcinoma starts in the glandular cells of the fallopian tubes.
What are the Causes of Fallopian Tube Cancer?
The precise causes of fallopian tube cancer are not entirely understood. However, several factors may increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Age: The risk of fallopian tube cancer increases with age, particularly in postmenopausal women.
- Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast or fallopian tube cancer can elevate the risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in certain genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, associated with breast and ovarian cancers, can also increase the risk of fallopian tube cancer.
- Reproductive Factors: Women who have never been pregnant or have had few or no pregnancies have a slightly higher risk.
What are the Symptoms of Fallopian Tube Cancer?
The symptoms of fallopian tube cancer can be vague and similar to other gynaecological conditions. Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: Such as postmenopausal bleeding or irregular menstrual bleeding.
- Pelvic pain or pressure: Often persistent and not relieved by typical interventions.
- Abdominal bloating or swelling: Due to the presence of a mass or fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits: Such as increased frequency or discomfort during urination.
- Unexplained weight loss: Often accompanied by loss of appetite or fatigue.
Does Fallopian Tube Cancer Affect Fertility?
Fallopian tube cancer and its treatment can significantly impact fertility. Due to the aggressive nature of this cancer, treatment often involves surgery, including removal of the affected fallopian tubes and possibly the ovaries and uterus. This can lead to infertility or early menopause.
How is Fallopian Tube Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of fallopian tube cancer typically involves several steps:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination: Detailed discussion of symptoms, medical history, and a pelvic examination.
2. Imaging Studies: This includes transvaginal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or PET scan to visualize the fallopian tubes and surrounding structures.
3. Biopsy: A tissue sample from the suspicious area is taken and analyzed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
How is Fallopian Tube Cancer Treated?
The treatment for fallopian tube cancer depends on the stage and extent of the disease. Common approaches include:
1. Surgery: This involves the removal of the affected fallopian tube, ovaries, uterus, and surrounding tissues (salpingo-oophorectomy and hysterectomy).
2. Chemotherapy: Administered after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
3. Radiation Therapy: Utilized in some cases to destroy cancer cells or alleviate symptoms.
4. Targeted Therapy: Medications that specifically target cancer cells may be used in certain advanced cases.
Conclusion
Fallopian tube cancer is a rare but serious condition that primarily affects postmenopausal women. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for improving outcomes. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatment options can empower individuals and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding prevention, screening, and management.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it