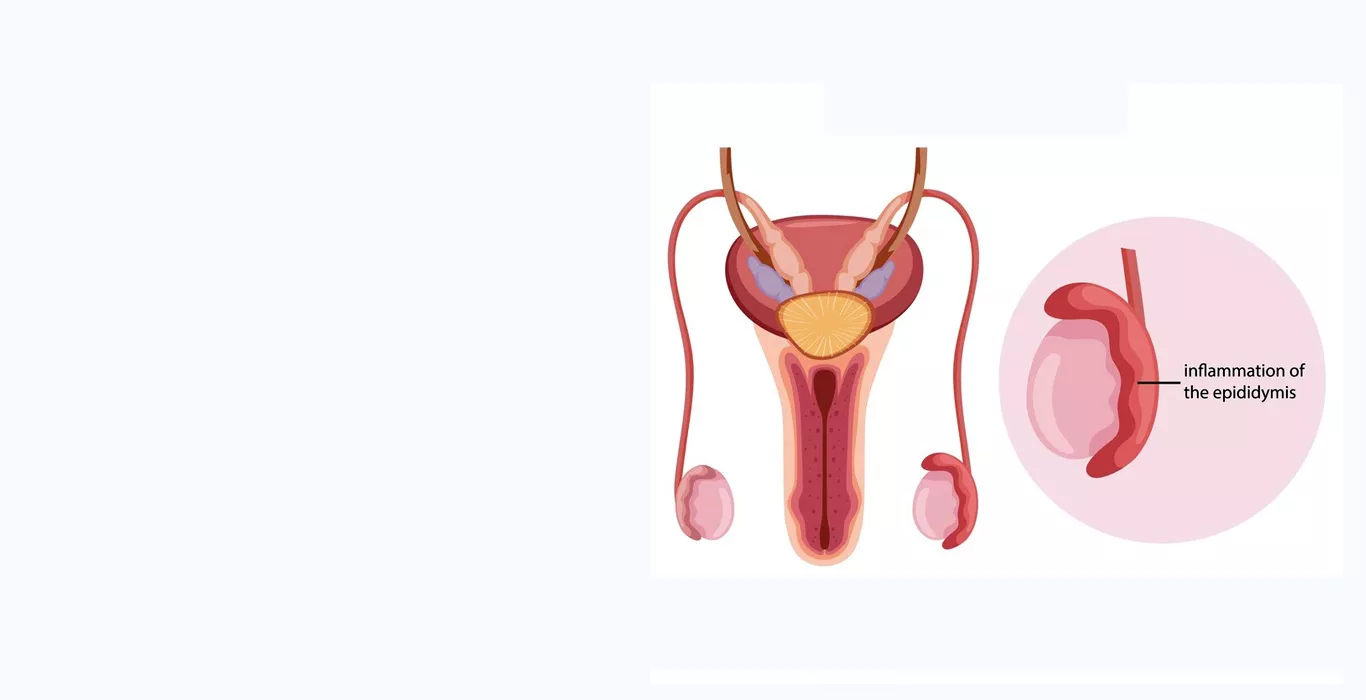
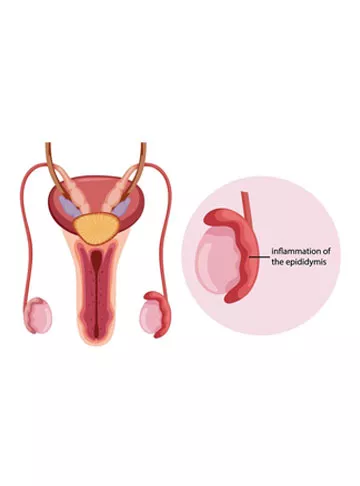
What is Epididymitis?
Epididymitis is the inflammation or infection of the epididymis, a crucial structure responsible for storing and transporting sperm. The epididymis is a narrow, twisted tube located at the back of each testicle, and it connects the testes to the vas deferens, the tube through which sperm passes during ejaculation. When the epididymis becomes inflamed or infected, it can lead to pain, swelling, and other uncomfortable symptoms.
Who can get Epididymitis?
Epididymitis can affect males of all ages, but it is most common in young adults and older men. Sexually active males, especially those under the age of 35, are at a higher risk of developing epididymitis. Additionally, individuals with a history of urinary tract infections (UTIs), prostate infections, or previous episodes of epididymitis are also more prone to this condition.
What are the Types of Epididymitis?
Epididymitis can be classified into two main types:
1.Acute Epididymitis: This type develops suddenly and is characterized by severe pain, swelling, and inflammation. It often occurs due to bacterial infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or urinary tract infections (UTIs).
2.Chronic Epididymitis: Chronic epididymitis involves persistent or recurring symptoms lasting for more than six weeks. The pain associated with chronic epididymitis is usually less severe than in the acute form, but it can be long-lasting and affect a person's quality of life.
What are the Causes of Epididymitis?
Epididymitis is typically caused by a bacterial infection, which can be triggered by various factors:
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Common STIs such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia can lead to epididymitis, especially in sexually active individuals.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacteria from a UTI can sometimes travel through the urethra and cause epididymitis.
- Prostate Infections: Infections in the prostate can spread to the epididymis, causing inflammation.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma to the groin area or injury to the testicles can also result in epididymitis.
What are the Symptoms of Epididymitis?
The symptoms of epididymitis can vary in intensity and may include:
- Pain and Tenderness: Typically, there is pain and tenderness in one or both testicles, often accompanied by swelling and redness.
- Fever and Chills: In some cases, individuals with epididymitis may experience fever and chills.
- Frequent Urination and Painful Urination: These symptoms may be present, especially if the cause is a urinary tract infection.
- Discharge from the Penis: If the cause is an STI, there might be discharge from the penis.
Does Epididymitis Affect Fertility?
Epididymitis can potentially affect fertility. The epididymis is a crucial part of the male reproductive system, as it stores and transports sperm. Inflammation or infection of the epididymis can lead to scarring or blockages, interfering with the sperm's ability to travel and resulting in fertility problems. Prompt treatment and management of epididymitis are essential to minimize the risk of fertility issues.
How is Epididymitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing epididymitis involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, which may include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will discuss the symptoms, and medical history, and conduct a physical examination to assess the swelling, tenderness, and overall condition of the testicles.
- Urinalysis and Blood Tests: These tests can help identify the presence of infection or inflammation.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound may be performed to visualize the epididymis and testicles, helping to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
How is Epididymitis Treated?
The treatment of epididymitis typically involves a combination of medication, rest, and lifestyle modifications:
- Antibiotics: If the infection is bacterial, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Pain Management: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting and elevating the scrotum may help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Ice Packs: Applying ice packs to the affected area can also provide relief from pain and swelling.
Conclusion
Epididymitis is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and potential fertility issues. It's important for individuals experiencing symptoms of epididymitis to seek prompt medical attention for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to manage and prevent epididymitis effectively.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it