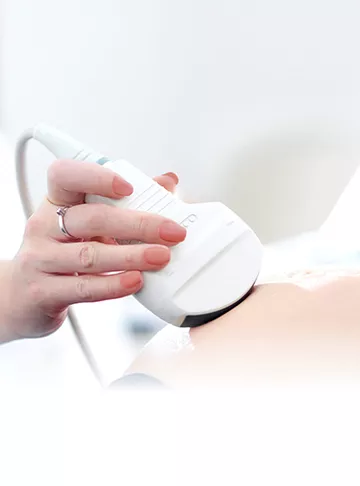
What is Ultrasound (or Sonography)?
Sonography or ultrasound is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images (a sonogram) of the inside of the body. It is also referred to as diagnostic medical sonography.
Pregnancy Calculator Tools for Confident and Stress-Free Pregnancy Planning
Get quick understanding of your fertility cycle and accordingly make a schedule to track it
Get a free consultation!
© 2025 Indira IVF Hospital Private Limited. All Rights Reserved. T&C Apply | Privacy Policy| *Disclaimer